The Portal








Artificial intelligence is the future.
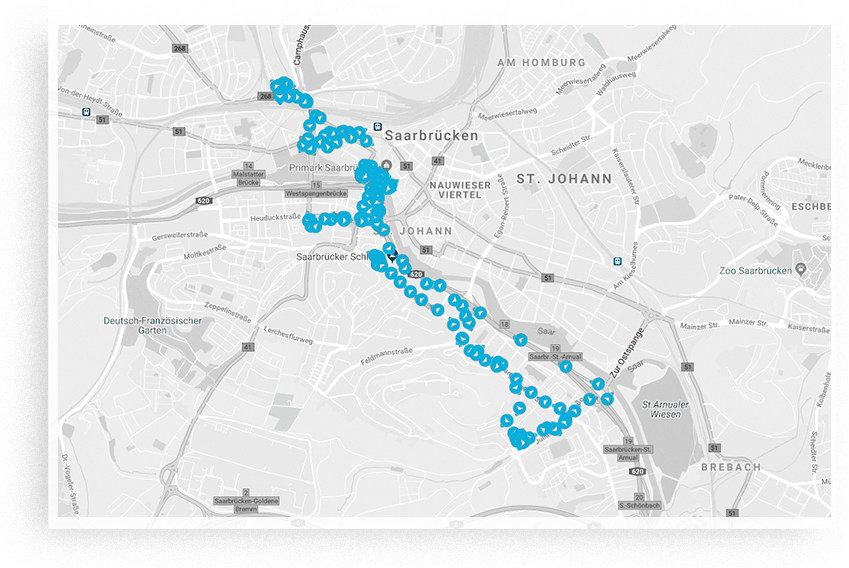
Satellite-based positioning systems and individual tracking solutions
for your everyday life and your business here and now.
WHAT IS WHAT?
2G, 3G, 4G und 5G
The shortcuts 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G are the different mobile radio standards.
The G stands for Generation and thus designates the second, third, fourth and fifth generation of mobile radio standards.
__________
The difference between 2G, 3G and 4G lies mainly in the speed of data transmission. This is important on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets with SIM cards in order to surf the Internet as quickly as possible. 5G is due to be launched at the end of 2019.
__________
The first 5G compatible smartphones are already on the market. Initially, however, the faster Internet will only be available in a few major German cities.
Common data rates
2G
GPRS : max. 53,6 kbit/s
Edge: up to 220 kbit/s
__________
3G/UMTS
HSDPA: up to 42 Mbit/s
__________
4G/LTE
CAT 0
max. Download: 1 MBit/s
max. Upload: 1 MBit/s
_______
CAT 1
max. Download: 10 MBit/s
max. Upload: 5 MBit/s
_______
CAT 2
max. Download: 50 MBit/s
max. Upload: 25 MBit/s
_______
CAT 3
max. Download: 100 MBit/s
max. Upload: 50 MBit/s
_______
CAT 4
max. Download: 150 MBit/s
max. Upload: 50 MBit/s
_______
CAT 5
max. Download: 300 MBit/s
max. Upload: 75 MBit/s
_______
CAT 6
max. Download: 300 MBit/s
max. Upload: 50 MBit/s
_______
CAT 7
max. Download: 300 MBit/s
max. Upload: 100 MBit/s
_______
CAT 8
max. Download: 300 MBit/s
max. Upload: 150 MBit/s
_______
CAT 9
max. Download: 450 MBit/s
max. Upload: 50 MBit/s
_______
CAT 10
max. Download: 450 MBit/s
max. Upload: 100 MBit/s
LTE-Cat-NB1 / NB-IoT – NarrowBand-IoT
LTE-Cat-NB1 is a specification of 3GPP and is also known as NarrowBand-IoT (NB-IoT) and NB-LTE. LTE network operators can use LTE-Cat-NB1 to optimize their mobile networks for typical Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
__________
LTE-Cat-NB1 operates at 800 and 900 MHz frequencies with wide coverage and good penetration of buildings. The technology uses the existing infrastructure of the LTE and GSM network providers, whereby a single mobile radio cell with NB-IoT technology can network up to 50,000 objects in parallel.
__________
The radio modules are simpler in design compared to LTE and require less energy, so some applications could do without a button cell for several years.






